- Dr. Shaheer Hamza
MBBS, MD (Anesth), FIPM
Consultant Anaesthesiologist & Pain Physician - 04933 262262 (Malappuram)
- 0491 2576436 (Palakkad)
- cordialpainclinic@gmail.com
Migraine
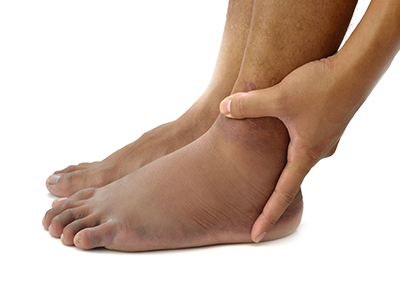
Burning Feet Syndrome
April 28, 2022
What is rheumatoid arthritis (RA)?
April 28, 2022A migraine is a headache that can cause severe throbbing pain or a pulsing sensation, usually on one side of the head. It’s often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and extreme sensitivity to light and sound.
Migraine triggers
- Hormonal changes in women. Fluctuations in estrogen, such as before or during menstrual periods, pregnancy and menopause, seem to trigger headaches in many women.
- These include alcohol, wine, and too much caffeine, such as coffee.
- Stress at work or home can cause migraines.
- Sensory stimuli. Bright or flashing lights can induce migraines, as can loud sounds. Strong smells — such as perfume, paint thinner, secondhand smoke and others — trigger migraines in some people.
- Sleep changes. Missing sleep or getting too much sleep can trigger migraines in some people.
- Physical factors. Intense physical exertion might provoke migraines.
- Weather changes. A change of weather or barometric pressure can prompt a migraine.
- Oral contraceptives and vasodilators, such as nitroglycerin, can aggravate migraines.
- Aged cheeses and salty and processed foods might trigger migraines. So might skipping meals.
- Food additives. These include the sweetener aspartame and the preservative monosodium glutamate (MSG), found in many foods.
Risk factors
Several factors make you more prone to having migraines, including:
- Family history. If you have a family member with migraines, then you have a good chance of developing them too.
- Migraines can begin at any age, though the first often occurs during adolescence.
- Women are three times more likely than men to have migraines.
- Hormonal changes. For women who have migraines, headaches might begin just before or shortly after onset of menstruation. They might also change during pregnancy or menopause.
Symptoms
- Usually Unilateral throbbing Headache aggravated on bending forward and mostly moderate to severe in intensity.
- Usually lasts between 15 mins to 2 hours.
- Nausea and rarely vomiting
- Increased sensitivity to light and sound. Normal light seems too bright. Normal conversation may seem too loud.
Treatment Options
Lifestyle Modification: Developing a regularity in day to day activities ie a daily routine is key to successful management.
- Healthy diet
- Regular exercise
- Avoidance of caffeine, alcohol, smoking
- Identification of stressors and consciously avoiding them as far as possible
- Treatment of Acute Attacks:
- Acute attacks usually respond well to paracetamol and even better to NSAIDs like Ibuprofen which are readily available over the counter.
- Specific drugs are available, which are very effective. However these drugs should be taken only on advice of your pain physician as they have adverse effects and interactions with few common medications.
- Interventional Pain Management for Migraine: Interventional techniques are not commonly used, however few modalities like Occipital nerve block, Sphenopalatine ganglion blockade, trigger point injections are used in exceptional cases.
Non Surgical Migraine Treatment at Cordial Pain Clinic:
- Consultation and Pharmacotherapy
- Dietary and lifestyle modification advice
- Interventional techniques like Occipital Nerve Block, Sphenopalatine Ganglion Block, Trigger point injections
Migraine is a chronic pain disorder but not a life threatening disease. It does not worsen with age or culminate into some other dangerous disorder. Although not completely curable, it is definitely treatable and manageable.
Book an appointment today at Cordial Pain Clinic and take the next step towards a pain-free life!.